Neurodevelopmental disorders
Dysgraphia

Neurodevelopmental disorders
Dysgraphia
- Home
- Learning disabilities
- Dysgraphia
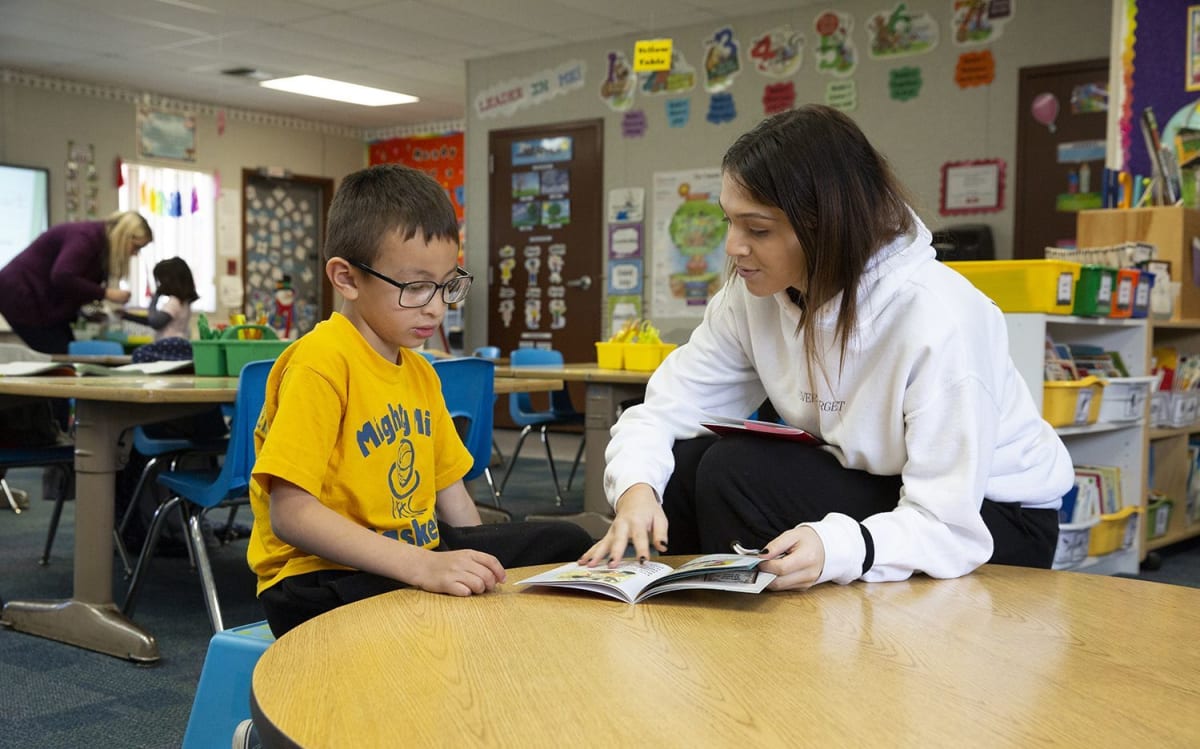
What is Dysgraphia?
Dysgraphia is a neurological disorder of written expression that impairs writing ability and fine motor skills. It is a learning disability that affects children and adults, and interferes with practically all aspects of the writing process, including spelling, legibility, word spacing and sizing, and expression.
Prognosis for Dysgraphia
One of the main signs of dysgraphia is messy handwriting. Here are some of the key handwriting skills people with dysgraphia may struggle with:
- Tight, awkward pencil grip and body position
- Illegible handwriting
Avoiding writing or drawing tasks - Tiring quickly while writing
Saying words out loud while writing - Unfinished or omitted words in sentences
- Difficulty organizing thoughts on paper
- Difficulty with syntax structure and grammar
- A large gap between written ideas and understanding is demonstrated through speech.
Treatments influence prognosis
There’s no cure for dysgraphia. Treatment varies from child to child and depends on whether they have any other learning disabilities or health conditions. Medication used to treat ADHD has helped with dysgraphia in some kids who have both conditions.
Early detection and early signs
The earlier therapy starts, the better. Kids may get these services for free at school. They may also get accommodations to keep dysgraphia from getting in the way of learning.
The diagnosis
Even though dysgraphia isn’t a formal diagnosis, the challenges with transcription are very real. And people who have them often need extra support to improve skills and manage the challenges.
Causes of Dysgraphia
In the case of children suffering from Dysgraphia, some researchers think one or both of the following steps in the process of writing go off track:
- Organizing information stored in their brain
- Getting words onto paper by writing or typing the characters
Common co-occurring conditions in Dysgraphia
Producing writing involves different motor skills. For example, people use fine motor skills for holding writing tools. They use gross motor skills for holding their arm in the right position. And they use motor planning for forming and spacing letters.
Having trouble with motor skills has a direct effect on transcription. Kids who have these challenges may be diagnosed with developmental coordination disorder (DCD).
- September 25, 2021
- 9:40 am